Recently, I've been playing a lot of Minecraft. Specifically, modded Minecraft, using a custom modpack for Cobblemon.
A friend of mine hosts a multiplayer server on the Apex hosting platform, but has given me access to administrate the server in case issues arise.
Unfortunately, issues do arise, and fairly frequently, particularly involving mod crashes.
To fix these, I usually have to either edit player data, or world data, using an Named Binary Tag (NBT) editor.
Doing so however, does not address the root cause of the issue, which is usually caused by the mod developers forgetting to add error handling somewhere.
Modifying a Minecraft mod may seem daunting at first, but is actually pretty easy when using the correct tools.
Recaf
One such tool, is Recaf by coley, a modern Java bytecode editor.
Recaf is capable of both decompilation and recompilation, which means that, to some extent, the source code of the mod can be reconstructed and viewed.
Recaf can also deobfuscate code, using various mappings.
Unfortunately, during my adventures, I failed to recompile my edited Java source code, so I had to resort to editing the bytecode directly.
Recaf GUI
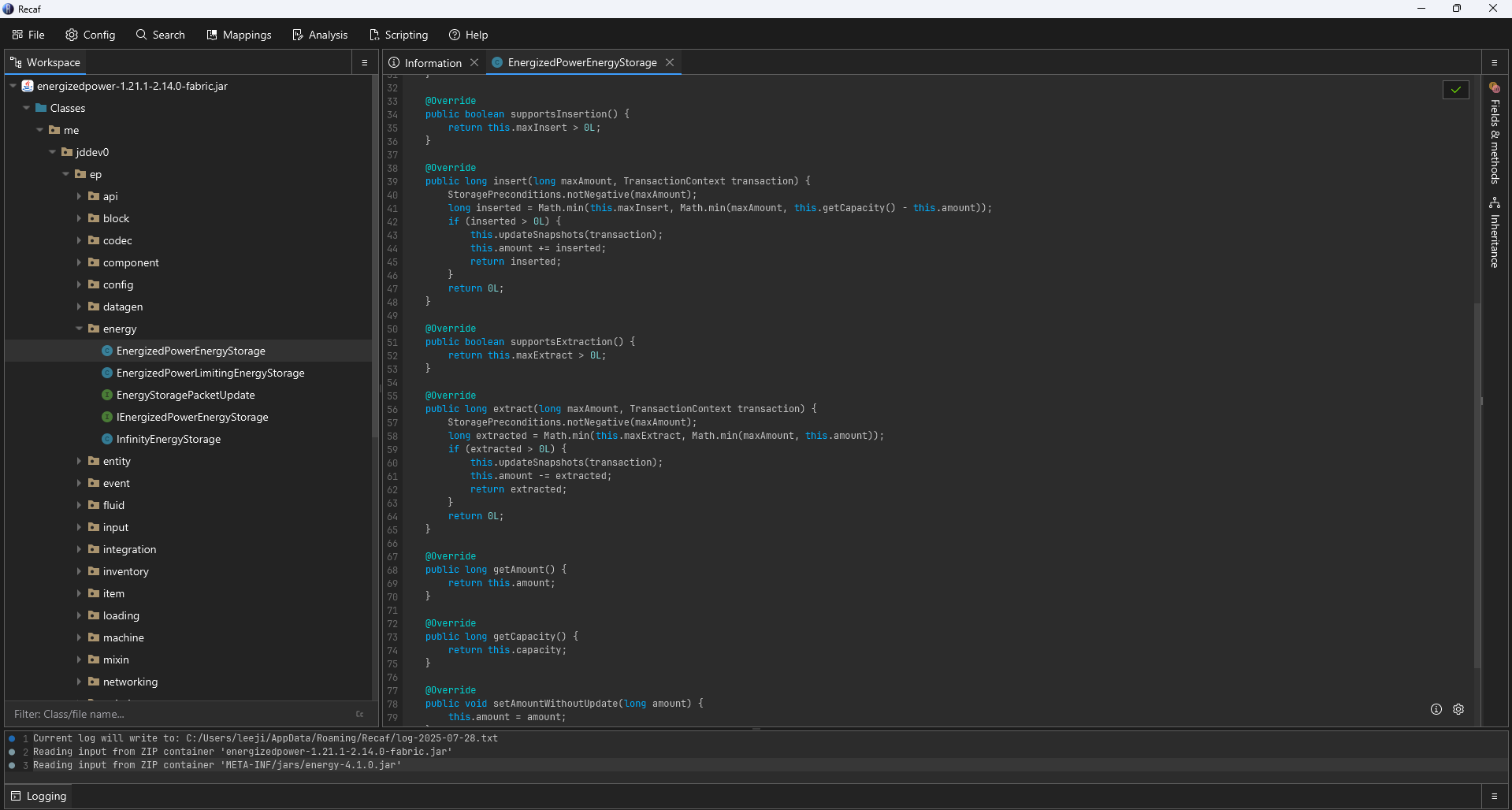
Energized Power Crash
For some reason, the solar panel from the Energized Power mod tried to extract a negative amount of energy from itself, which triggered an unhandled IllegalArgumentException, causing the server to crash.
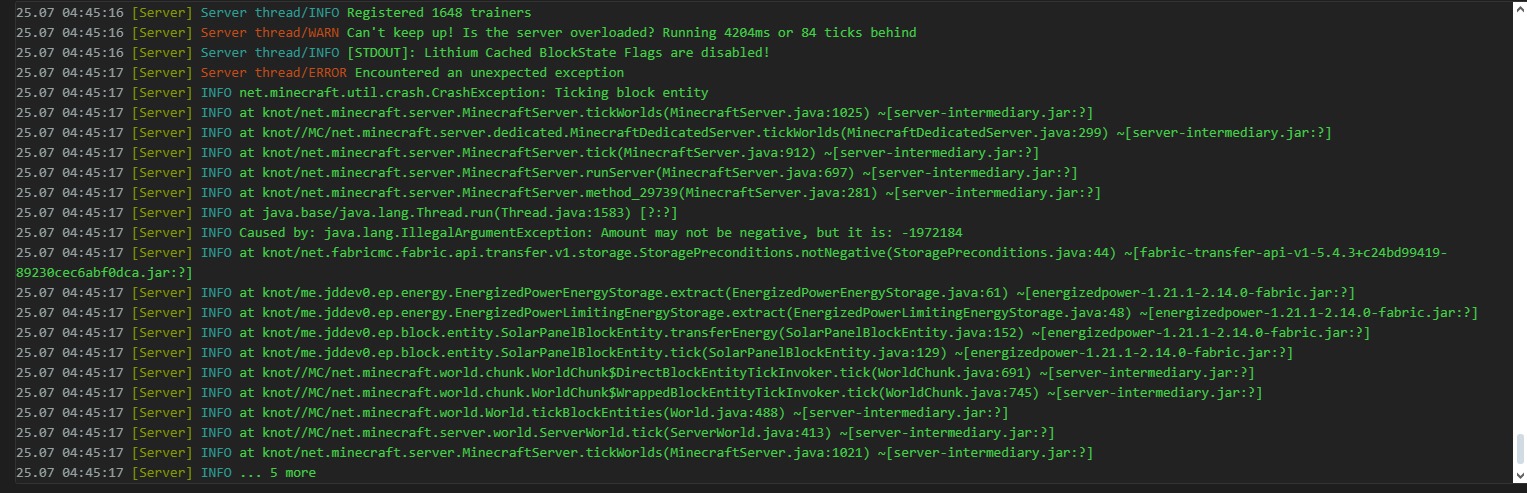
To fix this, all one needs to do is clamp the values between 0 and the provided amount, preventing negative values from ever occuring.
The reconstructed source code for the crashing function in question:
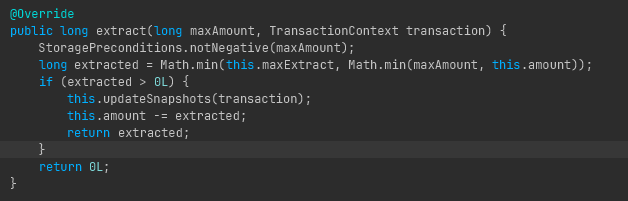
Unfortunately, after coding in the fix, I failed to compile the modified code due to missing libraries, which I found to be too much of a pain to resolve.
So instead, I resorted to editing the bytecode directly, which is like, assembler/assembly for the Java programming language.
Original Bytecode Snippet
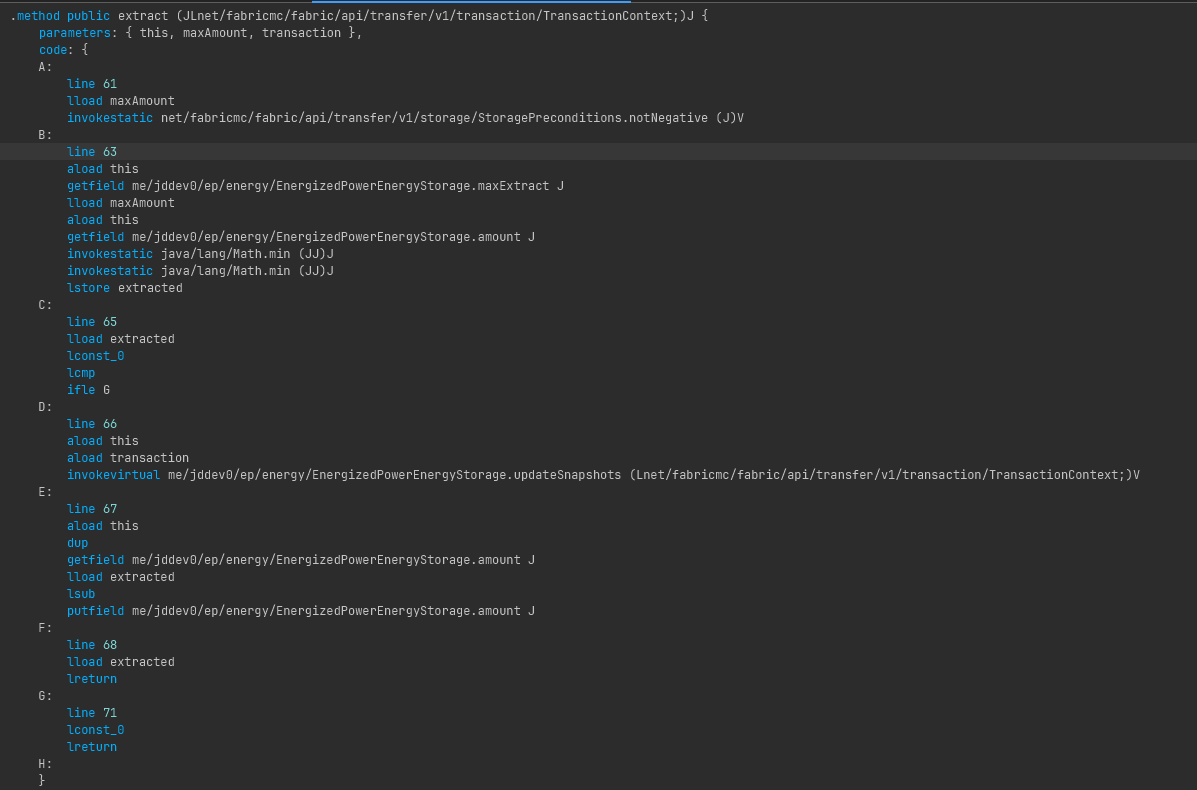
I don't know Java bytecode, so I enlisted the help of an LLM (Gemini 2.5 Flash) to speed things up, like everyone does these days.
A:
line 61
lload maxAmount
lconst_0
lcmp
ifge MOD_SKIP_CLAMP
lconst_0
lstore maxAmount
MOD_SKIP_CLAMP:
lload maxAmount
invokestatic net/fabricmc/fabric/api/transfer/v1/storage/StoragePreconditions.notNegative (J)VAnd viola, it no longer crashes.
More Resources for Recaf
BONUS: Connecting to a Minecraft server running on WSL locally
So I wanted to test out my changes in a local server, so I don't accidentally brick the live one.
After copying over all the files, I tried to run the server.jar from the Windows command line.
Frustratingly, it just doesn't work on Windows, and I don't have a Linux server just lying around (I should get one), so I had to resort to using WSL instead.
Running the server works like a charm, but connecting to it from the Minecraft Client is another hurdle.
Unfortunately, one does not simply connect to a server running on WSL using localhost from Windows.
Instead, I had to find the IP Address for the WSL instance, using the command: "wsl hostname -I".
Read more about that here (Microsoft Docs).
Final Step
There's one more step before we can actually connect to our Minecraft server, we have to configure the Windows Firewall (sigh).
So here's some vibe advice from Gemini:
Configure Windows Firewall (Essential!):
Even for local connections, Windows Firewall might block the connection. You need to create an inbound rule to allow traffic on the Minecraft port (default 25565).
Open "Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security" (search for it in the Start Menu).
In the left pane, select "Inbound Rules."
In the right pane, click "New Rule..."
Select "Port" and click "Next."
Choose "TCP" and enter 25565 (or your custom port) in "Specific local ports." Click "Next."
Select "Allow the connection" and click "Next."
Choose the network profiles where this rule should apply (e.g., "Private" for your home network). Click "Next."
Give the rule a name (e.g., "Minecraft WSL Server") and an optional description. Click "Finish."
And we're done.